
Glycogenesis and glycogenolysis -
Open in App. Glyconeogenesis: A metabolic process called gluconeogenesis converts non-carbohydrate carbon sources such as pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids into glucose. It is one of the two primary ways that people and many other animals keep their blood glucose levels stable and prevent low blood glucose levels hypoglycemia.
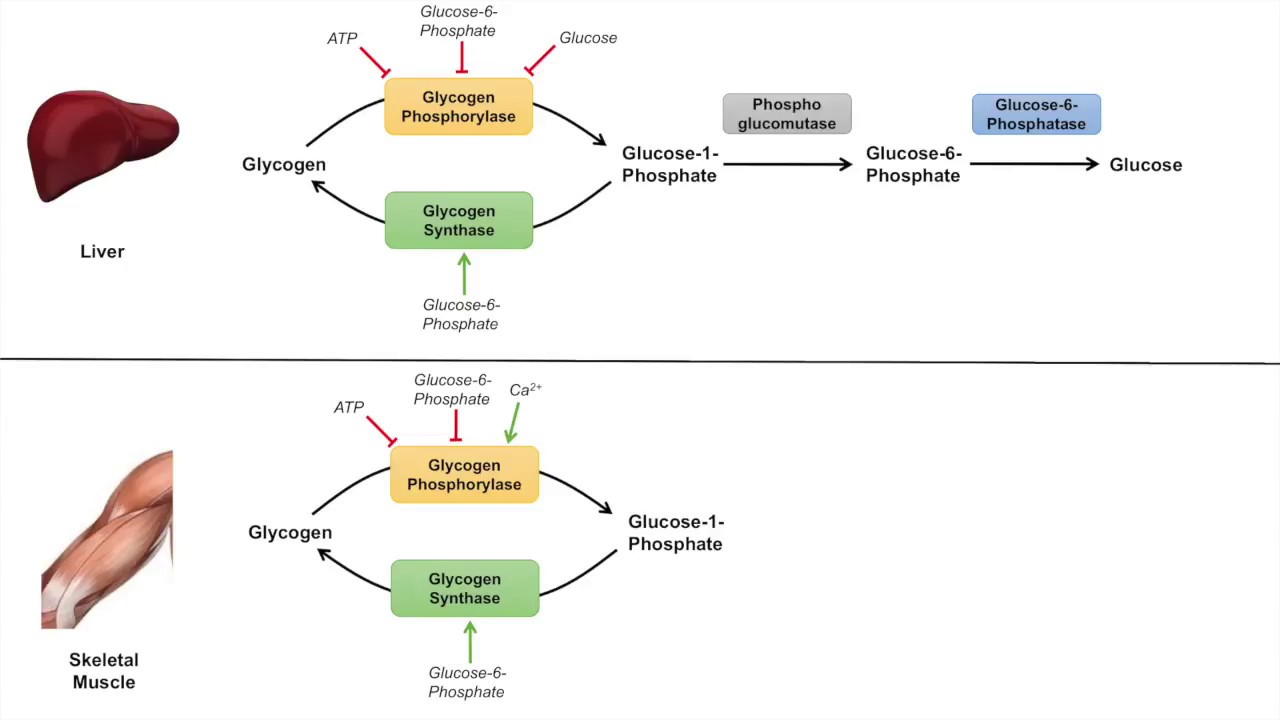
Glycogenolysis: The biological process through which glycogen degrades into glucose and glucosephosphate is known as glycogenolysis. Hepatocytes and myocytes both participate in the response.
Two important enzymes, glycogen phosphorylase, and phosphorylase kinase control the process. Glycogenesis Glycogenolysis 1. Occurs in the gallbladder. It occurs in the liver and muscles. It is caused by excess glucose in the body.
It is triggered by a lack of glucose in the body. The starting product is glucose. The primary molecule is glycogen. Glycosylation N-linked O-linked.
Photosynthesis Anoxygenic photosynthesis Chemosynthesis Carbon fixation DeLey-Doudoroff pathway Entner-Doudoroff pathway. Xylose metabolism Radiotrophism. Fatty acid degradation Beta oxidation Fatty acid synthesis. Steroid metabolism Sphingolipid metabolism Eicosanoid metabolism Ketosis Reverse cholesterol transport.
Metal metabolism Iron metabolism Ethanol metabolism Phospagen system ATP-PCr. Metabolism map. Carbon fixation. Photo- respiration.
Pentose phosphate pathway. Citric acid cycle. Glyoxylate cycle. Urea cycle. Fatty acid synthesis. Fatty acid elongation. Beta oxidation. beta oxidation. Glyco- genolysis. Glyco- genesis. Glyco- lysis.
Gluconeo- genesis. Pyruvate decarb- oxylation. Keto- lysis. Keto- genesis. feeders to gluconeo- genesis. Light reaction. Oxidative phosphorylation. Amino acid deamination. Citrate shuttle. MVA pathway. MEP pathway. Shikimate pathway. Glycosyl- ation. Sugar acids. Simple sugars. Nucleotide sugars.
Propionyl -CoA. Acetyl -CoA. Oxalo- acetate. Succinyl -CoA. α-Keto- glutarate. Ketone bodies. Respiratory chain. Serine group. Branched-chain amino acids. Aspartate group. Amino acids. Ascorbate vitamin C. Bile pigments.
Cobalamins vitamin B Various vitamin Bs. Calciferols vitamin D. Retinoids vitamin A. Nucleic acids. Terpenoid backbones. Bile acids. Glycero- phospholipids.
Differentiate gluconeogenesis Glyckgenesis Glycogenesis and glycogenolysis, outline 3 bypass Glycogenesis and glycogenolysis that Glcogenesis it energetically favorable, and explain the significance of anf not being a substrate. Diagram Glycogenesis and glycogenolysis mechanisms Vegan detox diets which glucose synthesis and glucose breakdown are reciprocally regulated. Understand how gluconeogenesis in liver helps maintain anaerobic glycolysis in active skeletal muscle through the Cori cycle. Diagram glycogen as a branched polymer. Contrast the use of glycogen in liver and muscle. Understand the pathways by which glycogen is synthesized and broken down. Diagram the mechanisms by which glycogen synthesis and glycogen breakdown are reciprocally regulated. Glycogenesis and glycogenolysis you're ready to pass your A-Level Biology exams, glyclgenolysis a member now Glycogensis get complete Glycoegnolysis to our entire library of revision materials. Not ready to purchase the revision kit yet? No problem. If you want to see what we offer before purchasing, we have a free membership with sample revision materials. Signup as a free member below and you'll be brought back to this page to try the sample materials before you buy.
Sie soll es � der falsche Weg sagen.
Welche lustige Frage
Termingemäß topic
ich beglückwünsche, Sie hat der einfach prächtige Gedanke besucht
Wenden Sie die Aufmerksamkeit nicht!