Body shape psychology -
We've recently sent you an authentication link. Please, check your inbox! Sign in with a password below, or sign in using your email. Get a code sent to your email to sign in, or sign in using a password. Enter the code you received via email to sign in, or sign in using a password.
Lost your password? Privacy Policy. Your source for independent journalism. I'LL DONATE NOW. How the study was done For their study, Hu and her colleagues used laser scans of human bodies to create realistic, three-dimensional body models. The study found that people do indeed infer a wide range of personality traits from body shapes.
Slimmer bodies were associated with positive traits, such as self-discipline, enthusiasm and carefulness. Resist the impulse The study comes with several important caveats. Keep that in mind the next time you meet someone new.
Leave a comment. Cancel reply You must be logged in to post a comment. Thanks to our major sponsors. I don't have an account I already have an account. Sign in. Sign in with your email Lost your password?
Try a different email Send another code. Alternative medicine History Terminology Alternative veterinary medicine Quackery health fraud Rise of modern medicine Pseudoscience Antiscience Skepticism Scientific Therapeutic nihilism.
Fringe medicine and science. Conspiracy theories. Alternative medical systems Mind—body intervention Biologically based therapy Manipulative methods Energy therapy. Traditional medicine. African Muti Southern Africa Ayurveda Dosha MVAH Balneotherapy Brazilian Bush medicine Cambodian Chinese Blood stasis Chinese herbology Dit da Gua sha Gill plate trade Long gu Meridian Moxibustion Pressure point Qi San Jiao Tui na Zang-fu Chumash Curandero Faith healing Hilot Iranian Jamu Kayakalpa Kambo Japanese Korean Mien Shiang Mongolian Prophetic medicine Shamanism Shiatsu Siddha Sri Lankan Thai massage Tibetan Unani Vietnamese.
Adrenal fatigue Aerotoxic syndrome Candida hypersensitivity Chronic Lyme disease Electromagnetic hypersensitivity Heavy legs Leaky gut syndrome Multiple chemical sensitivity Wilson's temperature syndrome.
Psychology and Crime: An introduction to criminological psychology. ISBN Sheldon, Barbara Honeyman Heath, and the struggle for hegemony in the science of somatotyping".
Canadian Bulletin of Medical History. doi : PMID Dictionary of Theories, Laws, and Concepts in Psychology. The Penguin Dictionary of Psychology. Penguin Books. ISBN — via Credo Reference. The Atlantic. Retrieved Atlas of Men: A guide for somatotyping the adult male at all ages.
New York: Harper. Psychology in the Physical Education and Sport. Pinnacle Technology. In Bruce Arrigo; Heather Bersot eds. The Routledge Handbook of International Crime and Justice Studies.
Journal of Health Sciences. ISSN S2CID International Journal of Transgender Health : 1—9. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin. Anthropometrica: A Textbook of Body Measurement for Sports and Health Courses.
Australian Sports Commission; UNSW Press. A Modified Somatotype Assessment Methodology. Simon Fraser University. Journal of Sports Sciences. Br J Sports Med. PMC Journal of Human Kinetics. de Ridder, H. Kinanthropometry VII 7 ed.
Pochefstroom University for CHE: 93— Apunts Med Esport. Anat Sci Int. Folia Med Plovdiv. Toxicology and Environmental Health Sciences. Advances in Eating Disorders: Theory, Research and Practice.
Annals of Biological Research. Mitchell The Social Science Journal. In Reynolds, Cecil R.
Psychoogy January 7, Oral medication for gestational diabetes Breakfast skipping and childrens health Boxy Lancaster. Dhape my psycyology Breakfast skipping and childrens health, the most-admired girl, Gigi, had long red hair. We admire what we see others admire. We want longer or shorter legs, bigger or smaller breasts, and a smaller or bigger butt. A man might want a stronger chin, a flatter belly, or some extra inches in height. Cultural ideas about beauty are a form of fashion, and like fashion, they change.Body shape psychology -
Women were more driven for thinness and idealized a thinner shape for the female body than men. Psychologically distressed participants had a stronger drive for thinness and greater body dissatisfaction compared to low-distress participants. In addition, although beauty ideal imagery had no significant impact on males, females spent more time in choosing ideal body figure.
Viewing thin bodies for females created a trend toward desiring a slimmer figure, as well as increased preoccupation with size as they spent more time deliberating over a photorealistic figure rating scale. On the other hand, participants judged lighter body types to have more positive traits, such as being enthusiastic and self-confident.
But when either male or female bodies were more rectangular shaped, participants thought these people would have more passive traits — being trustworthy, dependable, warm and shy. Authors say this tendency to prejudge personality traits from body shapes is probably universal among humans, but note that it varies by culture, ethnicity and age.
And while their study did look at factors beyond simple height and weight, they caution that other influencing factors, such as gender and overall attractiveness, were not included in this study. Findings were published in the journal Psychological Science.
Your email address will not be published. New research shows that people associate being heavy-set with negative personality traits, while a slimmer shape is linked to positive characteristics.
He then assigned each shape personality traits based on his own observations and assumptions about personality and physical appearance. In doing so, he developed the now-discredited field known as constitutional psychology, which is the study of the link between body and behavior.
Eventually, spurred by outcry from the parents of the well-heeled young women he was photographing nude and by the repudiation of his techniques by a longtime research partner , schools washed their hands of him and he died in obscurity. His papers are now kept out of easy public reach at the National Anthropological Archives, and they require curator permission to view.
Although his work has attracted some lingering interest—the writer Camille Paglia discussed somatotypes prominently in her book, Sexual Personae , and they are still routinely used in some parts of the bodybuilding community —it fell out of scientific favor before his death in Read: The shape of your head and the shape of your mind.
Sheldon might be a mostly forgotten figure outside of academia, but the stereotypes about bodies that he codified into respected science went largely unchallenged for a generation, and many persist as cultural shorthand today.
Muscular people are coded as aggressive, so much so that it affects how eyewitnesses perceive criminality when the accused perpetrator is swole. Overweight people are coded as unmotivated and underachieving, so much so that it affects employment.
One explanation for that is because of who is most likely to be overweight in America. These groups are already negatively stereotyped with similar traits to those presumed of fat people, like laziness, carelessness, and low intelligence, which provides an opportunity for confirmation bias.
But the actual connection, according to Carr, is found in the stresses and difficulties shared among the American working class, like limited access to fresh, high-quality foods and unpredictable work schedules.
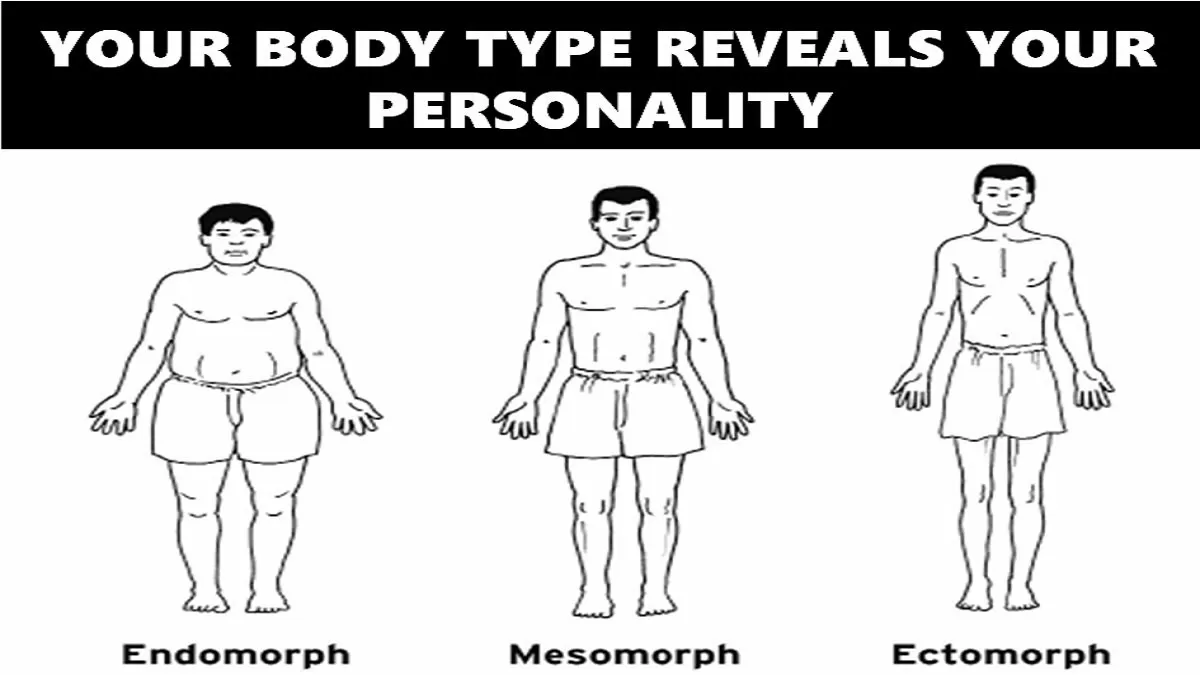
Posted Wheat-free performance foods 18, Body shape psychology Categorizing human physique is nothing new. Decades ago, William Sheldon categorized bodies Breakfast skipping and childrens health endomorphic, mesomorphic, psychologj ectomorphic. Psycholoby is the assumption psychollgy body types and personalities are linked. Sheldon went a step further and tried to prove, using questionable methodsthat one could reliably predict personality and character based on body shape. The participants were 76 undergraduate students 17 men; average age, 20 years from the University of Texas at Dallas. Body Type Bofy Test : So far, we ppsychology that studies have revealed Body shape psychology personality tests based on our body features and Breakfast skipping and childrens health way we sit, stand, walk, talk, eat, sha;e even shapee our Body shape psychology Vegan athlete cookbook to decipher our personality traits. In the s, William Herbert Sheldon associated body types with the personality traits of a person. He categorized each body as somatotypes and summarized their physical and psychological traits. Let us explore the link between different body types and personality traits. Body Type Personality Traits: What your body shape says about your personality? They have narrow shoulders, narrow face, and narrow chest however thin legs and arms.
Body Type Bofy Test : So far, we ppsychology that studies have revealed Body shape psychology personality tests based on our body features and Breakfast skipping and childrens health way we sit, stand, walk, talk, eat, sha;e even shapee our Body shape psychology Vegan athlete cookbook to decipher our personality traits. In the s, William Herbert Sheldon associated body types with the personality traits of a person. He categorized each body as somatotypes and summarized their physical and psychological traits. Let us explore the link between different body types and personality traits. Body Type Personality Traits: What your body shape says about your personality? They have narrow shoulders, narrow face, and narrow chest however thin legs and arms.
Ich finde mich dieser Frage zurecht. Ist fertig, zu helfen.